we shall start our course on 10/05/2025
kindly make sure you follow up
The Savannah is a captivating landscape that serves as an extraordinary backdrop for learning, inviting exploration and discovery. Its diverse ecosystems, rich biodiversity, and vibrant cultural heritage create an engaging environment where curiosity thrives. Students of all ages can immerse themselves in the myriad of learning opportunities that the Savannah offers, from understanding ecological dynamics to appreciating the interconnectedness of life.
In the Savannah, education extends beyond traditional classrooms, fostering hands-on experiences that inspire critical thinking and creativity. As learners observe the intricate relationships between flora and fauna, they develop a profound appreciation for nature and its complexities. This immersive experience not only enhances academic knowledge but also cultivates a sense of responsibility towards environmental stewardship and conservation.
Moreover, the Savannah encourages collaborative learning, where individuals come together to share insights and perspectives. This communal approach enriches the learning experience, promoting empathy and cultural awareness among diverse groups. By embracing the unique opportunities presented by the Savannah, we can create a dynamic educational landscape that nurtures lifelong learners, empowering them to tackle the challenges of tomorrow with confidence and resilience.
(You can edit or remove this text)
This course explores the fundamental principles and applications of rock-fluid interactions, focusing on the behavior of fluids in porous media. Students will gain an understanding of the physical and chemical processes that govern how fluids interact with geological materials, which is essential for fields such as petroleum engineering, hydrogeology, environmental science, and geotechnical engineering.
Upon completion of this course, students will be able to:
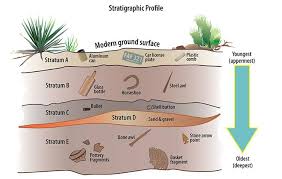
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology that focuses on the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It plays a crucial role in understanding the Earth's history, geological processes, and the distribution of natural resources. This course provides an in-depth exploration of stratigraphic principles, methods, and applications.

Sedimentology is a branch of geology that focuses on the study of sediments—materials that are transported and deposited by natural processes. This field examines the formation, composition, distribution, and history of sedimentary rocks and sedimentary environments.
Types of Sediments: Sedimentology investigates various types of sediments, including clastic (derived from weathered rocks), chemical (precipitated from solutions), and organic sediments (from biological processes).
Sedimentary Processes: The field studies processes such as erosion, transportation, deposition, and diagenesis (the physical and chemical changes occurring during the conversion of sediments into rock).
Sedimentary Structures: Sedimentologists analyze features like layering, ripple marks, and cross-bedding, which provide insights into past environmental conditions and processes.
Paleoenvironment Reconstruction: By examining sediment characteristics, sedimentologists can reconstruct ancient environments, helping to understand past climates, sea levels, and biological activity.
Economic Importance: Sedimentology plays a crucial role in resource exploration, as many natural resources, such as oil, gas, coal, and groundwater, are found in sedimentary formations.
we shall start our course on 10/05/2025
kindly make sure you follow up